12. SIEM Framework
SIEM Heading
SIEM
ND545 C02 L03 A13 SIEM
SIEM Notes
Recap:
SIEM Security Information and Event Management, it is an application that serves as a log aggregator and, more importantly, analyzes the logs to allow alerting, dashboard creation and efficient queries to run.
SIEMs allow you to retain your log data for much longer. In particular, networking equipment do not typically have much storage and logs are overwritten frequently.
Considerations when choosing your SIEM solution:
- Licensing what is the licensing model? Is it based on users, nodes or volume of events?
- Scalability should your organization experience rapid growth, can the solution keep up?
- Dashboards What built-in dashboards are included? How difficult is it to customize existing and make new dashboards?
- Alerts Is the solution capable of real-time alerting?
- ** Query Language** From an analyst point of view this may be the most important, how complicated is the query language and is there plentiful documentation available?
Should you choose Open Source or a Commercial SIEM?
Open Source:
Pros
- Highly Customizable.
- Generally have a strong community.
- Lack of restrictions on data ingestion
Cons
- Support is generally, not always, limited to community.
- Some open source SIEMs do not come with as many dashboards pre-configured as their commercial counterparts.
Commercial
Pros
- Support, part of the licensing fee includes a level of support.
- Save time. All SIEMs require extensive time commitments to setup but Commercial SIEMs are marginally more capable out of the box.
- Commercial SIEMs have more applications included and available.
Cons
- Price. Depending on how large your environment is and how much data is ingested, commercial SIEMs can be extremely expensive.
There are multiple methods of ingesting logs:
- Push this is where the source machine sends the logs to the SIEM.
- Pull this is where the destination, in this case the SIEM, requests the logs.
- Batch when files are pulled or pushed all at once in scheduled intervals this would be in batch form.
- Agent Many SIEMs now have agents that are deployed and keep the logs synchronized.
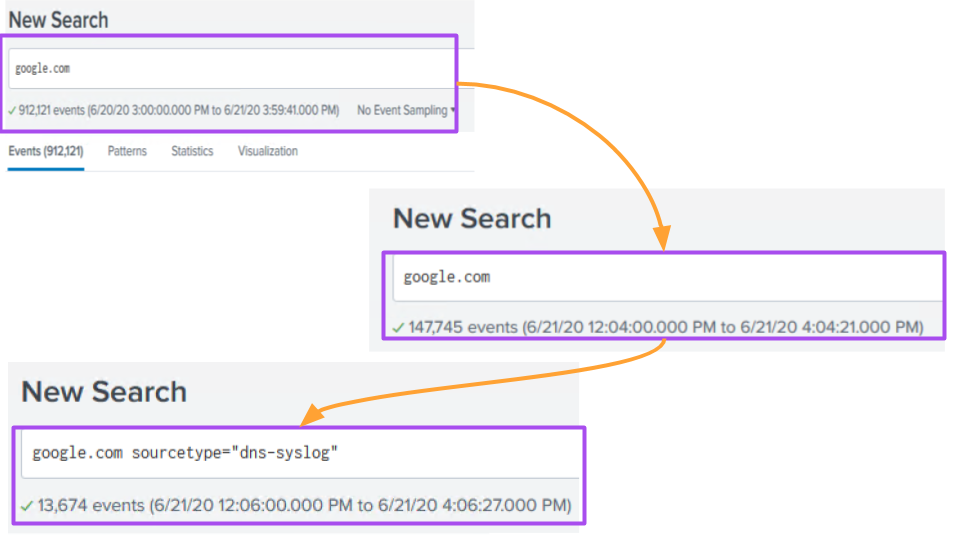
SIEM Query Strategies, the more specific the better!